What is female infertility?
Infertility is a disease that makes a person unable to get pregnant. For people assigned female at birth (AFAB), an infertility diagnosis comes after:
How common is female infertility?
Infertility is a common disease. At least 10% of women and people assigned female at birth deal with infertility of some kind. The chances of infertility increase with age.
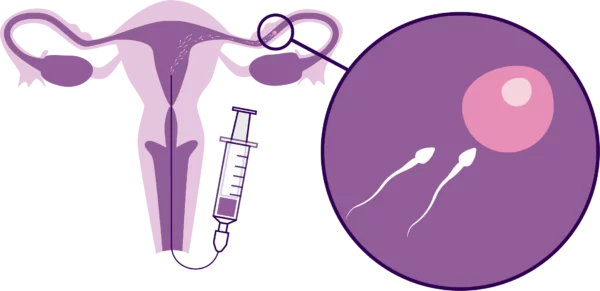
Female Infertility
Six months of trying to get pregnant if you’re older than 35.
One year of trying to get pregnant if you’re younger than 35.
Trying to get pregnant means you’re regularly having sex without birth control. Some people receive a diagnosis sooner if they have a medical condition or uterine factor infertility.
Causes of infertility can be due to either partner. In fact, infertility occurs due to a problem with the male reproductive system just as frequently as it occurs due to a problem with the female reproductive system.
Infertility in women can result from age, hormone conditions, medical conditions, and lifestyle or environmental factors.
When the cause of infertility is thought to come from the person with a uterus, healthcare professionals consider it female infertility or “female factor” infertility.
- How common is female infertility?
Infertility is a common disease. At least 10% of women and people assigned female at birth deal with infertility of some kind. The chances of infertility increase with age.
- Causes and Symptoms:
What are the signs of infertility in women?
The most common sign of infertility is being unable to get pregnant despite having regular, unprotected sex. Other signs may include absent or irregular periods.
- What causes female infertility?
There are many possible causes of infertility. However, it can be difficult to pinpoint the exact cause, and some couples have unexplained infertility. Some possible causes of female infertility can include:
Problems with your uterus: This includes uterine polyps, fibroids or adhesions (scarring) inside the cavity of your uterus. Polyps and fibroids can form on their own at any time. Adhesions can form after a surgery like a dilation and curettage (D&C).
Problems with your fallopian tubes: The most common cause of “tubal factor” infertility is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Untreated chlamydia and gonorrhea are common causes of PID. Endometriosis can also cause scarring of your fallopian tubes.
Problems with ovulation: There are many reasons why a person may not ovulate (release an egg) regularly. Hormonal imbalances, an eating disorder, substance use disorder, thyroid conditions, severe stress and pituitary tumors are all examples of things that can affect ovulation.
Problems with egg count and quality: You’re born with all the eggs you’ll ever have, and this supply can run out early, before the natural age of menopause (around 51). In addition, some eggs will have the wrong number of chromosomes and be unable to fertilize and grow into a healthy fetus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is secondary infertility in a woman?
Where is the sperm is collected?
The pricing of women’s health treatments should prioritize accessibility and affordability, ensuring that essential healthcare services, such as gynecological exams, prenatal care, contraception, and screenings for conditions like breast cancer and STDs, are within reach for all women. Our aim is to provide fair and transparent pricing, along with options for financial assistance, should be made available to promote women’s overall well-being and equality in healthcare.
Can a damaged womb conceive?
What is female sperm called?
In animals, female gametes are called ova or egg cells, and male gametes are called sperm. Ova and sperm are haploid cells, with each cell carrying only one copy of each chromosome.
